Sunbathe properly
In this article we would like to address the issue of vitamin D and Covid-19. Completely unnoticed by the mainstream media, research is being conducted in various places around the world on the effect of vitamin D deficiency on susceptibility to infection with corona viruses and the incidence of complications in covid-19 related to vitamin D.
READING TIP: Vitamin D deficiency in COVID-19 patients
A perennial issue is whether or what sunscreen to use. Sun exposure of the skin is the most natural source of vitamin D. Once a sunscreen is applied, this natural vitamin D formation is completely blocked.
In Central Europe, vitamin D deficiency is endemic. This means that a large part of the population is inadequately supplied with vitamin D. Senior citizens, children and people with dark skin are usually particularly affected. Due to our way of life, which is predominantly indoors, the majority of the population does not have sufficient direct exposure to sunlight, which is necessary for vitamin D formation. Vitamin D deficiency significantly increases the risk of contracting covid-19 and suffering a severe course of the disease. 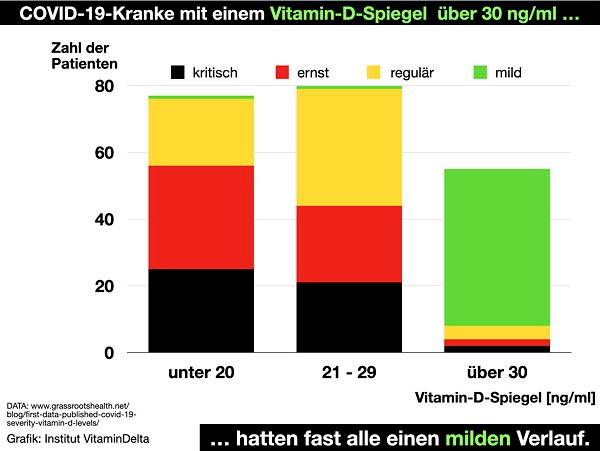
How much sun does a person need?
"Regular but restrained tanning without sunscreen is absolutely necessary," says Prof. Dr. Michael Holick from the USA. He has been researching exclusively on the subject of vitamin D and its effects in the human body for over 30 years. Sun exposure of the skin leads to the body's own production of vitamin D. However, for years doctors have been strongly advising against sunbathing without sunscreen. The reason is the risk of skin cancer, which is increased by excessive sun exposure. Research says that repeated sunburns of the skin increase the risk of both dark skin cancer (melanoma) and light skin cancer (basalioma).
Does the general recommendation to use sunscreen make sense?
The general recommendation nowadays is to apply a sunscreen before exposing oneself to the sun. This recommendation completely prevents vitamin D formation in the body. There are two risks to this approach:
- Vitamin D deficiency
- Toxic exposure of the body to the ingredients of sun creams
READING TIP: Vitamin D - the sun vitamin
A study of sunscreen ingredients shows that 90% of all sunscreens contain the UVB blocker octinoxate. Although this ingredient is effective in preventing sunburns, the prevention of malignant melanoma could not be proven with certainty until today. 40% of approved sunscreens impair male fertility. Most sunscreen products contain the active ingredient octinoxate or one of its derivatives. Octinoxate is an "endocrine disruptor", which means that it disrupts the hormone system and thus alters the normal functioning of the organism. Of the hormones, oestrogen, progesterone, the thyroid hormones and the male sex hormones are particularly affected.
Recommended sunscreen
There are a few sunscreens that contain zinc oxide or titanium oxide without nanoparticles. These are effective mineral sunscreens that are recommended along with some herbal products. Vegetable oils such as coconut oil or sesame oil are sunscreens with a sun protection factor below 10. Use only such sunscreens and avoid those with octinoxate-type biochemical UV blockers. Even the best sun cream only protects you from UV rays for a certain time, depending on the sun protection factor. If you are exposed to direct sunlight for a longer period of time while hiking, rowing, surfing, sunbathing, etc., only clothing will help as a suitable UV blocker.
How to sunbathe properly? 4
- In Central Europe for intensive vitamin D formation only possible from the end of March - mid-October between 11:00 - 15:00. The further you move on the time axis from the sun's peak (21 June), the smaller this time window becomes as well as the intensity of the penetrating UV-B radiation, closing in mid-October to the end of March.
- Depending on skin type, about 10-20 minutes (fair skin types need shorter time); longer exposure to the sun does nothing for vitamin D production.
- At least arms and legs unprotected
- Under cloudless skies
- Avoid sunburn and severe skin redness, this is a clear signal of overdose! Be especially careful when your skin has to get used to the sun again after winter.
- When using sunscreen, make sure that it provides UV-A and UV-B protection!
- Moderate and moderate
- Use the following links to find out how "strong" the sun's UV radiation is in your area (UV Index): UV Index Germany-wide | UV Index Europe-wide
- Caution when taking medication! Be aware of possible phototoxic side effects (package insert of the medication).
Extra tips for a "holiday in the sun "*.
- Follow the tips above
- Adjust your sun duration to the latitude of your holiday destination (intensity of UV radiation increases the closer you are to the equator).
- Find out about your UV index. You can see how "strong" the UV radiation of the sun is at your holiday destination or at home on the following links: UV Index Germany-wide | UV Index Europe-wide
Skin care after sunbathing
In times of strong sun exposure, Maharishi AyurVeda recommends regular oil massage. Suitable oils are virgin coconut oil and Pitta massage oil.
READING TIP: Carrying out the oil massage
Our recommendations for vitamin D therapy:
- Regularly check your vitamin D level (take a blood sample once a year!).
- Take vitamin D on days without direct sun exposure at midday
- Correctly dose vitamin D: 1000 i.U. vitamin D per 20kg body weight daily. Example: Body weight 70kg, vitamin D dose 4000 i.U. daily. If taken weekly (less recommended) 28 000 - 30 000 i.U. once a week.
Summary
Vitamin D has been shown to increase resistance to infections, including covid-19. Therefore, vitamin D should be taken by all people all year round. In summer, vitamin D intake can be temporarily replaced by CORRECT sunbathing. About 15 minutes of full-body sun exposure around noon is sufficient for this. Conventional sunscreens can have serious side effects and should be avoided, especially for children and those who wish to have children. Alternatives are mineral and herbal sunscreens or clothing to be used after 15 minutes of sun exposure.
Sources:
- Biesalski, H. K. (2020) ‘Vitamin D deficiency and co-morbidities in COVID-19 patients – A fatal relationship?’, NFS Journal. Elsevier GmbH, 20, pp. 10–21. doi: 10.1016/j.nfs.2020.06.001.
- Glinsky, G. V. (2020). Tripartite Combination of Candidate Pandemic Mitigation Agents: Vitamin D, Quercetin, and Estradiol Manifest Properties of Medicinal Agents for Targeted Mitigation of the COVID-19 Pandemic Defined by Genomics-Guided Tracing of SARS-CoV-2 Targets in Human Cells. Biomedicines, 8(5), 129. doi:10.3390/biomedicines8050129
- Laird, J. Rhodes, R.A. Kenny, Vitamin D and inflammation: potential implications for severity of Covid-19, Ir. Med. J. 113 (2020) 81.
- https://sonnenallianz.spitzen-praevention.com/richtig-sonnen/tipps-tricks/


Elvira de Pasqua schrieb am 31.07.2022
Liebe Drs Schachinger,
das sind wirklich wertvolle Tipps, vielen Dank dafür!!!
soma med Team schrieb am 02.08.2022
Sehr gerne!